Generative AI could “destroy” the $68 billion search engine optimization (SEO) industry, which is led by small and medium-sized businesses, according to Ravi Sen, an associate professor of information and operations management at Texas A&M University.
In an article published on the nonprofit media network The Conversation, Sen argues that the switch to artificial intelligence-fueled search by companies like Google, Microsoft, and China’s Baidu “could fundamentally change the online search ecosystem.”
Also read: Google Says Users Can Now Create AI Images Directly From the Search Bar
SEO scores may become ‘useless’
After the success of ChatGPT, big tech companies have stampeded to adopt generative AI, a type of artificial intelligence that can generate text, images, and translate languages. Google created Bard, Microsoft added AI to Bing, Baidu has Ernie, and DuckGoGo’s got DuckAssist.
By integrating AI, all the major search engines promise one thing: to make the internet search experience better for users. But Sen warns that websites, news outlets, blogs, and others that have relied on SEO for traffic for the past 25 years could be in trouble after the new changes.
“Over time, as the quality of AI-generated answers improves, users will have less incentive to browse through search result listings. They can save time and effort by reading the AI-generated response to their query,” said the Texas A&M University scholar.
“In other words, it would allow you to bypass all those paid links and costly efforts by websites to improve their SEO scores, rendering them useless,” he added.
SEO helps optimize websites and their content so they rank higher in search engine results pages. The technology, which has spawned an industry worth more than $68 billion, involves creating content that is relevant to the keywords that people are searching for on the Internet.
AI making things obsolete
A user searching for information online would typically type the things they are looking for in the search bar. The search engine returns a list of results, often from websites, where one can get the required information. Websites battle it out for the best-placed listing on Google, Bing, or other such search engines.
According to Sen, content creators utilize different strategies to attract users to their own websites, including SEO, paid placements, and banner displays. But AI makes it possible for search engines to create their own content, reducing the need for SEO altogether.
Sen demonstrated how Bing AI could be used to create an itinerary for a trip to Destin, Florida, based on the prompt, “Create a three-day itinerary for a visitor.” The bot replies with a detailed plan ‘instead of a bunch of links to Yelp and blog postings that require lots of clicking and reading.’
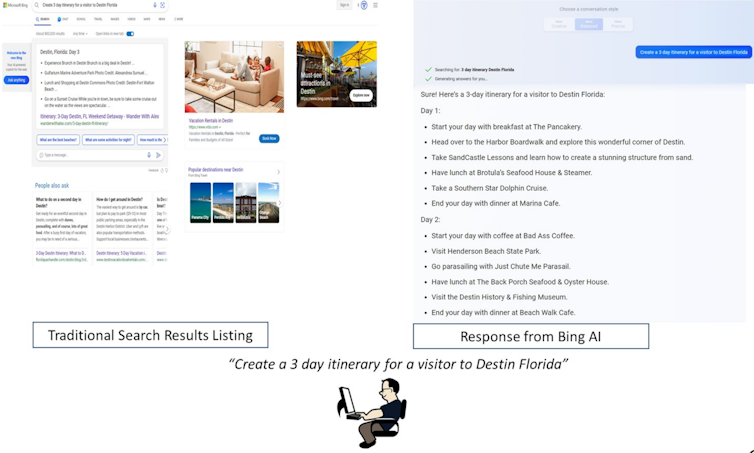
This is significant. As Ravi Sen pointed out, businesses may no longer feel the need to invest in SEO services if they can depend on search engines to provide their own material to users.
“Rather than getting a list of links, both organic and paid, based on whatever keywords or questions a user types in, generative AI will instead simply give you a text result in the form of an answer,” explains the Texas A&M University scholar.
“When users start ignoring the sponsored and editorial result listings, this will have an adverse impact on the revenues of SEO consultants, search engine marketing consultants, and, ultimately, the bottom line of search engines themselves.”

The financial impact
Sen expects the AI disruption of the SEO industry to have a major financial impact on search businesses, including dominant ones like Google and Microsoft that generate a lot of revenue from monetizing their online search services.
According to the 2023 SEO Global Strategic Business Report, the world market for search engine optimization was at $68.1 billion at the end of last year and is expected to reach $130 billion by 2030. The estimates were made prior to generative AI becoming a thing in search.
Sen, the Texas A&M University professor, said search engines “get a cut of the money that websites spend on improving their online visibility through paid placements, ads, affiliate marketing, and the like, collectively known as search engine marketing.”
In 2022, for example, $163 billion, or 58% of Google’s revenue, came from Google Ads, which provides such services. Search engines run by large entities like Google and Microsoft, “with many revenue streams, will likely find ways to offset the losses by coming up with strategies to make money off generative AI answers,” he stated.
“But the SEO marketers and consultants who depend on search engines—mostly small and medium-sized companies—will no longer be needed as they are today, and so the industry is unlikely to survive much longer,” Sen added.
Search engines are always working to improve the quality of their search results. So adopting AI to achieve those goals may be the logical thing to do. But questions still remain regarding the tendency of AI chatbots to “hallucinate” facts, providing false information with confidence.
It is something that’s made it difficult for humans to trust AI or even lend their loyalty to the technology, Sen says.









 and then
and then